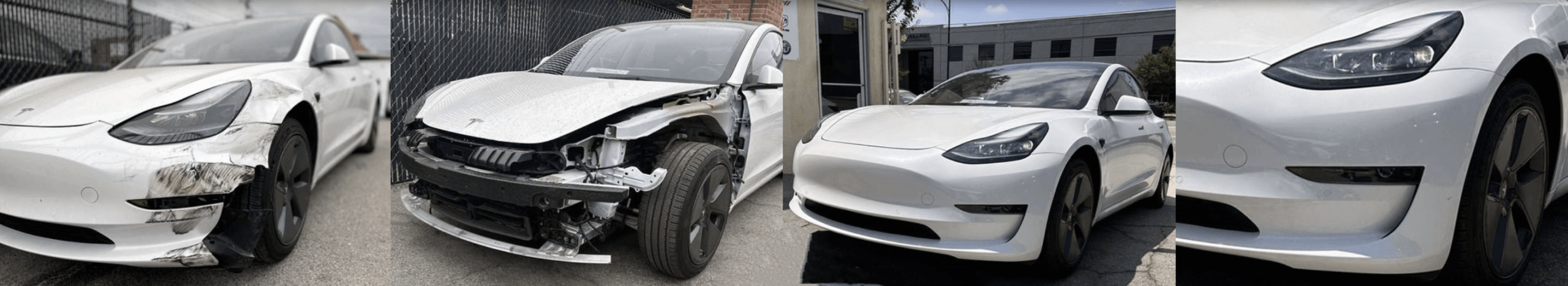
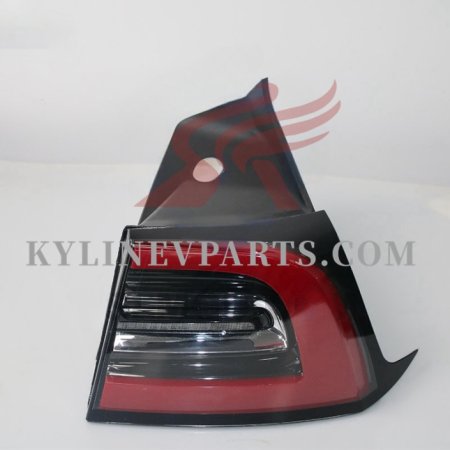
Tesla has revolutionized the automotive industry, emerging as a global leader in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing. With a product lineup that includes the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y, Tesla’s vehicles are renowned for their advanced technology, high-performance capabilities, and long-range driving.
As the global adoption of EVs continues to accelerate, the demand for Tesla vehicles is on the rise. This growth, in turn, has led to an increased need for replacement parts, making an understanding of Tesla replacement parts cost crucial for international dealers.
The primary objective of this article is to provide international dealers with a detailed and in-depth analysis of Tesla replacement parts cost. By exploring various aspects such as the factors influencing costs, cost comparisons across different models and parts categories, and strategies for cost-effective sourcing, dealers can make more informed decisions. This knowledge will not only help in setting competitive pricing but also in building sustainable business models in the highly competitive Tesla replacement parts cost market.
1. Technological Complexity and R&D Investment
1.1.1 Advanced Battery Technology
Tesla’s battery packs are at the forefront of EV technology. The company has invested heavily in research and development to create high-energy-density batteries with long-lasting performance. For example, the development of the lithium-ion battery technology used in Tesla vehicles involves complex engineering to optimize energy storage, charging speed, and battery life. This high level of technological sophistication means that battery replacement parts are expensive to produce. The cost of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are crucial for battery production, also fluctuates in the global market, directly impacting Tesla replacement parts cost.
1.1.2 Sophisticated Electrical and Autopilot Systems
Tesla vehicles are equipped with advanced electrical systems and the cutting-edge Autopilot technology. These systems require highly specialized components, such as sensors, control units, and software-integrated hardware. The research and development required to develop and maintain these systems is substantial.
For instance, the cameras and radar sensors used in the Autopilot system are designed to work in harmony with complex algorithms. Replacement parts for these systems are expensive due to the high level of engineering and calibration required, ensuring seamless integration with the vehicle’s overall electrical architecture.
1.2 Manufacturing and Quality Control
1.2.1 Precision Manufacturing Processes
Tesla employs precision manufacturing techniques to ensure the highest quality standards for its vehicles. The production of replacement parts, such as body panels made from lightweight yet strong materials like aluminum and carbon fiber composites, involves intricate manufacturing processes. These processes require specialized equipment and skilled labor.
For example, the manufacturing of a Tesla Model S aluminum body panel demands precise stamping and welding techniques to ensure a perfect fit and structural integrity. The high cost of this precision manufacturing is reflected Tesla replacement parts cost.
1.2.2 Stringent Quality Control Measures
Tesla has implemented rigorous quality control procedures at every stage of the manufacturing process. Replacement parts must meet the same exacting standards as the original parts installed in new vehicles. This includes multiple inspection points, performance testing, and compliance with international safety and environmental regulations. For instance, a replacement motor for a Tesla vehicle undergoes extensive performance testing to ensure it can deliver the same power and efficiency as the original. The cost of maintaining these stringent quality control measures adds to the overall Tesla replacement parts cost.
1.3 Supply Chain Dynamics
1.3.1 Global Sourcing of Raw Materials
Tesla sources raw materials from around the world for its replacement parts production. The company depends on a complex global supply chain for materials like rare earth elements, which are used in electric motors and other components. Fluctuations in the availability and cost of these raw materials in different regions can significantly impact the cost of replacement parts.
For example, if there are geopolitical tensions in a region that supplies a significant amount of a particular rare earth element, it can lead to supply disruptions and price increases, ultimately affecting the cost of parts that rely on that element.
1.3.2 Logistics and Distribution Costs
The transportation of replacement parts from manufacturing facilities to international dealerships also contributes to the overall cost. Tesla has to manage a vast logistics network to ensure the timely delivery of parts. Shipping costs, customs duties, and warehousing expenses all play a role.
For example, shipping a large and heavy battery pack from a manufacturing plant in the United States to a dealership in Europe incurs significant freight charges. Additionally, customs regulations in different countries can add extra costs in the form of duties and taxes, further driving up the price of replacement parts for international dealers.
1.4 Market Demand and Competition
1.4.1 Brand Monopoly and After-sales Market Control
Tesla has a certain degree of brand monopoly in the EV market, and it also has strong control over the after-sales parts market. In the early stages, Tesla’s replacement parts were mainly supplied by official channels, and the number of third-party manufacturers that could produce compatible parts was small. This situation made Tesla have strong pricing power in the replacement parts market, and Tesla replacement parts cost was relatively high.
1.4.2 Impact of Third-party Parts Manufacturers
With the continuous growth of Tesla’s market share, more and more third-party manufacturers have begun to enter the field of Tesla replacement parts production. These manufacturers, by virtue of lower production costs and flexible market strategies, have brought certain impacts to the cost of Tesla replacement parts. For example, some third-party manufacturers can produce body accessories and some simple electrical components with similar quality to the original parts at a lower cost, which, to a certain extent, has alleviated the high pressure of Tesla replacement parts cost.
2. Major Tesla Replacement Parts Cost
2.1 Battery Replacement Costs
2.1.1 Model-Specific Cost Breakdown
Model S:
The Tesla Model S, being one of the flagship models, has a relatively high-capacity battery. The cost of a battery replacement for a Model S typically ranges from $12,000 to $15,500 for the battery itself. This cost can vary depending on the battery size (such as 75 kWh, 100 kWh, etc.) and the model year. Labor costs for replacing a Model S battery at a Tesla service center, which usually charge around $175-200 per hour, can add another $525-2,600 to the bill, considering the replacement process may take 3-13 hours. So, in total, a Model S battery replacement can cost between $13,000-22,000.
Model 3:
For the more affordable Model 3, the battery replacement cost is somewhat lower but still significant. The cost of a new Model 3 battery pack, which comes in sizes ranging from 50 kWh to 82 kWh, is estimated to be around $7,000-$12,000. Labor costs for a Model 3 battery replacement, with service center rates of approximately $185-$200 per hour and a replacement time of 3-6 hours for uncomplicated cases, can amount to $600-$1,200. However, if there is damage to the battery pack and surrounding parts, the replacement time can extend to over 15 hours, increasing labor costs substantially.
Model X & Model Y:
The Model X, with its unique design and larger size, has a battery replacement cost similar to that of the Model S, given their comparable battery technologies and capacities. The Model Y, as a more recent addition to the Tesla lineup, also has battery replacement costs in a similar range to the Model 3, but it may vary slightly depending on market demand and production volumes.
2.2 Motor and Transmission System Replacement Costs
2.2.1 Tesla Replacement Parts Cost Differences Between Models
The cost of motor and transmission system replacement parts varies among different Tesla models. The Model S and Model X, which are positioned as high-end models, are equipped with more powerful motors and complex transmission systems, so their replacement parts cost more. For example, the replacement cost of a Model S motor is usually between $6,000 and $10,000, while the labor cost for replacement is about $1,500-$3,000. The Model 3 and Model Y, as mass-market models, have relatively simple motor and transmission system structures, and their replacement part costs are lower, with the motor replacement cost generally ranging from $4,000 to $7,000, and the labor cost being about $800-$1,500.
2.3 Body and Chassis Replacement Costs
2.3.1 Tesla Replacement Parts Cost of Key Components
Body and chassis replacement parts include body panels, suspension systems, braking systems, etc. The cost of these parts is affected by materials and manufacturing processes. For example, the aluminum alloy body panels used in Tesla vehicles have the advantages of light weight and high strength, but their manufacturing cost is high, and the replacement cost of a single body panel is usually between $500 and 2,000.
The suspension system parts, such as shock absorbers and springs, have different costs due to different models and configurations. The replacement cost of a set of suspension systems for Model S is about $3,000-5,000, while that for Model 3 is about $2,000-3,500.
2.3.2 Impact of Accident Damage on Replacement Costs
Accident damage is an important factor leading to the replacement of body and chassis parts. Severe accident damage may require replacing multiple parts at the same time, which will significantly increase the total replacement cost. For example, if a Tesla vehicle is involved in a frontal collision, it may be necessary to replace the front bumper, hood, front fenders, and even the front suspension system. The total replacement cost in such cases can reach tens of thousands of dollars. In addition, the difficulty of repairing damaged parts will also affect the labor cost. The more complex the damage, the higher the labor cost.
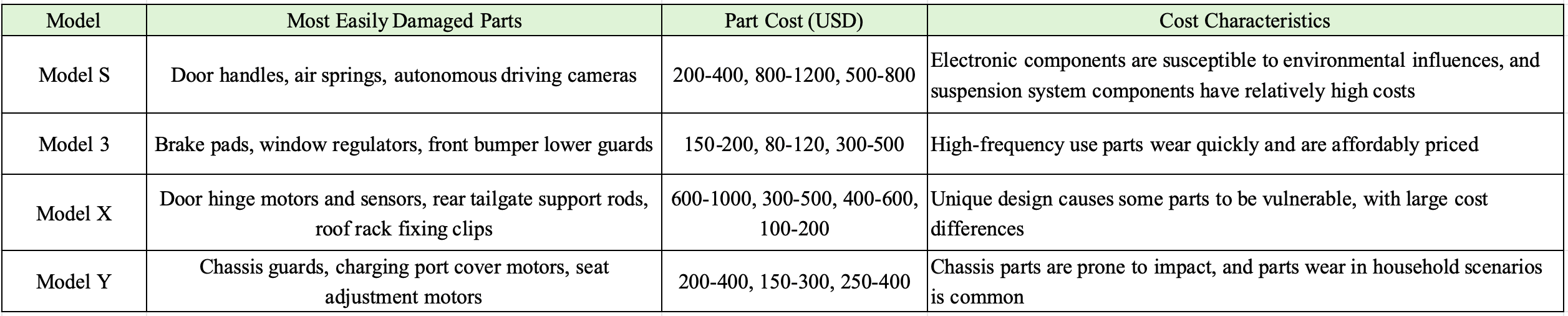
2.4 Most Easily Damaged Parts of Different Models
Model S
The most easily damaged parts of Model S include door handles (the electronic inductive design is prone to failure due to frequent use or low-temperature environments, with a replacement cost of about $200-400), air springs of the suspension system (prone to aging and air leakage after long-term use, with a single cost of about $800-1200), and autonomous driving cameras (located in the front grille or rearview mirror, easily damaged by collisions, with a single cost of about $500-800).
Model 3
The vulnerable parts of Model 3 mainly include brake pads (fast wear due to frequent braking in urban road conditions, with a single set cost of $150-200), window regulators (high motor failure rate, cost about $80-120), and front bumper lower guards (low design prone to scratches, replacement cost $300-500).
Model X
Due to the unique falcon wing door design of Model X, its door hinge motors and sensors are easily damaged (single motor cost about $600-1000, sensor about $300-500); in addition, the rear tailgate support rods (electric hydraulic type prone to oil leakage) and roof rack fixing clips (frequent disassembly and assembly leading to loosening and damage) are also high-frequency replacement parts, with costs of $400-600 and $100-200 respectively.
Model Y
The vulnerable parts of Model Y are concentrated in the chassis and electrical accessories, such as chassis guards (easily damaged by gravel impact, cost $200-400), charging port cover motors (failure due to frequent opening and closing, cost $150-300), and seat adjustment motors (wear due to frequent use in household scenarios, single cost $250-400).
3. Cost Comparison with Other Brands
3.1 Comparison with Traditional Fuel Vehicle Brands
Compared with traditional fuel vehicle brands, Tesla’s replacement parts cost generally shows a higher trend. Taking the engine/motor and battery-related parts as examples, the replacement cost of a traditional fuel vehicle engine is usually between $3,000 and 8,000, while Tesla’s motor replacement cost is usually higher than this range.
In terms of battery, traditional fuel vehicles do not have a large-capacity battery like Tesla, and the replacement cost of their small batteries for starting is only a few hundred dollars, which is far lower than the cost of Tesla’s battery replacement parts. However, in terms of some mechanical parts with low technical content, such as door handles and window regulators, the cost difference between Tesla and traditional fuel vehicle brands is not significant.
3.2 Comparison with Other New Energy Vehicle Brands
In the field of new energy vehicles, the cost of Tesla’s replacement parts is also at a relatively high level compared with some other brands. For example, the battery replacement cost of some domestic new energy vehicle brands in China is usually between $3,000 and 7,000, which is lower than that of Tesla.
This is mainly because these brands have lower R&D investment in battery technology and adopt more mature and low-cost battery solutions. However, compared with some other high-end new energy vehicle brands, Tesla’s replacement parts cost is certainly competitive. For instance, the replacement cost of some key components of a certain luxury new energy vehicle brand is even 20%-30% higher than that of Tesla.
4. Strategies for International Dealers to Reduce Tesla Replacement Parts Costs
4.1 Establishing Stable Cooperative Relations with Suppliers
International dealers can establish long-term and stable cooperative relations with Tesla’s official suppliers or qualified third-party manufacturers. By signing large-volume purchase agreements, they can obtain more favorable purchase prices.
For example, if a dealer can guarantee a certain annual purchase volume of battery replacement parts, the supplier may offer a discount of 5%-10% on the basis of the original price. In addition, stable cooperation can also ensure the stability of parts supply and reduce the impact of supply chain disruptions on costs.
4.2 Optimizing Inventory Management
Reasonable inventory management can reduce the cost of capital occupation and warehousing. Dealers can analyze the historical sales data and market demand of various replacement parts, predict the demand for parts in the next period, and formulate a scientific inventory plan. For example, for replacement parts with high demand and stable sales, such as some common body accessories, appropriate inventory can be maintained; for parts with low demand and high cost, such as some complex electrical components, they can adopt a just-in-time procurement mode to reduce inventory pressure.
4.3 Strengthening After-sales Service Capabilities
Improving the after-sales service capabilities of the dealer’s own team can reduce the cost of outsourcing services. By training technicians to master the professional skills of Tesla replacement parts installation and maintenance, dealers can complete the replacement and repair work independently, reducing the reliance on Tesla’s official service centers or other high-cost service providers. For example, after professional training, technicians can replace the motor and battery of Tesla vehicles by themselves, which can save a lot of labor costs compared with outsourcing.
4.4 Exploring Multichannel Sourcing
In addition to Tesla’s official channels, international dealers can also explore qualified third-party parts suppliers. Some third-party manufacturers can produce replacement parts that meet the quality standards at a lower cost, which can effectively reduce the procurement cost. However, dealers must strictly inspect the quality of third-party parts to ensure that they meet the safety and performance requirements of Tesla vehicles. For example, some third-party manufacturers have obtained relevant certifications and can produce high-quality body panels and suspension system parts, which are 15%-20% cheaper than the official parts.
5. The Impact of Tesla Replacement Parts Costs on Dealers’ Pricing Strategies
5.1 Cost is the core benchmark of pricing, determining the price floor
Tesla replacement parts cost directly from the “floor” of dealers’ pricing. Dealers must add storage, labor installation, operation, and other costs to the parts procurement cost (including raw materials, manufacturing, logistics, etc.), plus target profits, to form the final retail price. For example, the battery replacement cost (including parts and labor) for Model S is about $13,000-22,000. If dealers want to maintain a 20% gross profit margin, the retail price must be set above $15,600-26,400; below this floor, losses will occur.
This cost rigidity forces dealers to accurately calculate the balance of “cost + profit” in pricing: high-priced parts (such as motors, batteries) need to reserve higher profit margins to cover capital occupation costs, but also need to avoid excessive pricing leading to customer loss; low-cost vulnerable parts (such as brake pads, wipers) can adopt a “low-margin high-volume” strategy, attracting customers with a lower markup rate while increasing the overall repurchase rate.
5.2 Differences in Tesla Replacement Parts Cost drive pricing stratification to match customer needs
The Tesla Replacement Parts Cost differences between different parts (such as the huge cost gap between vulnerable parts and core components) prompt dealers to adopt a “stratified pricing” strategy to match the needs and payment willingness of different customers.
High-frequency vulnerable parts: low price and customer-friendly to seize the market
For example, vulnerable parts such as brake pads (single set cost about $150-200) and window regulators (cost about $80-120) for Model 3, due to high replacement frequency and high customer price sensitivity, dealers usually only add 10%-15%, pricing at $165-230 (brake pads) and $88-138 (window regulators). This low-price strategy can attract customers to repurchase frequently, and at the same time increase overall revenue through “parts + installation” packages (such as brake pads + installation fee totaling $250).
Core high-value parts: premium pricing with value-added services
For core components such as batteries (Model Y costs about $7,000-12,000) and motors (Model S costs about $6,000-10,000), due to high costs and strong technical barriers, customers pay more attention to quality and reliability rather than pure price.
Dealers usually add 20%-30%, pricing at $8,400-15,600 (Model Y battery) and $7,200-13,000 (Model S motor), while bundling services such as “1-year warranty + free inspection” to make customers feel the premium is reasonable.)
5.3 Cost fluctuations force pricing flexibility to balance profits and customer retention
Tesla parts costs are volatile due to factors such as raw materials (e.g., lithium, rare earths) and supply chains (e.g., rising logistics costs), which require dealers’ pricing strategies to be flexible.
Short-term cost increases: phased price adjustments or “hidden price increases”
If the cost of Model 3 batteries rises from $7,000 to 8,000 due to rising lithium prices, dealers may trigger customer dissatisfaction if they directly increase the retail price from $8,400 (original 20% markup) to $9,600 (new 20% markup).
At this time, “phased price adjustment” (first to $8,900, then to $9,600 after 3 months) or “hidden price increase” (keeping the part price unchanged but increasing the installation fee from $600 to 800) can be adopted to reduce customer resistance.
Long-term cost reduction: price reduction promotions or “value-added without price increase”
If third-party motor manufacturers increase production capacity, reducing Model Y motor costs from $5,000 to $4,500, dealers can reduce the retail price from $6,000 (original 20% markup) to $5,400 to attract more customers through price reductions; or keep the $6,000 price but offer a free motor inspection service (cost about $200) to enhance customer perceived value with “value-added without price increase”.
5.4 Cost transparency affects pricing trust, requiring both “reasonableness” and “transparency”
Foreign customers have high requirements for pricing transparency, and Tesla parts costs (especially official channels) are relatively public, which forces dealers’ pricing strategies to balance “cost reasonableness” and “price transparency” to build long-term trust.
For example, dealers can proactively show customers the “cost breakdown” when quoting (e.g., Model S battery: purchase price $12,000 + storage fee $500 + installation fee $1,000 = total cost $13,500, retail price $16,200, 20% gross margin), so that customers understand the pricing logic. For third-party parts, they can compare official parts costs (e.g., official body panel $1,500, third-party $1,200), price at $1,440 (20% markup), and emphasize “same quality as official, 10% lower price” to enhance pricing persuasiveness.
With the continuous development of Tesla’s technology and the expansion of production scale, it is expected that the Tesla Replacement Parts Cost will show a downward trend in the future. At the same time, the intensification of market competition and the maturity of third-party parts markets will also promote the rationalization of Tesla Replacement Parts Cost. International dealers should pay close attention to these changes, formulate flexible procurement and sales strategies, and improve their own competitiveness in the Tesla Replacement Parts Cost market.
Kylin EV Parts Ltd is located in Guangzhou, the hub of China’s automotive parts industry. focusing on the integration of Tesla, VW, and BYD, as well as aftermarket modifications. As China’s premier B2B supplier, we offer a comprehensive service in integrating EV spare parts for numerous foreign sellers, both online and offline.